What's The “J” In UNJ Screw Threads?
Dec 26, 2022
UNJ, UNJC, UNJF and UNJEF threads are almost identical to UN, UNC, UNF, and UNEF threads except that the external J thread has a much larger root radius than the standard UN threads and inspection must be performed on this element. The Special UNJ threads are designated by the nomenclature UNJS. J screw threads feature a root radius which improves the tensile stress area of the fastener and helps to reduce the stress concentration factor in the thread thus making the thread stronger. Additionally, the requirement for high strength is achieved with 3A and 3B classes of fit. All pitch diametersand tolerances are based on the Unified Inch Standard.
SAE AS8879 was introduced to provide an alternative to the inactive government specification Mil-S-8879 for screw threads – UNJ profile, inches.
Per SAE AS8879, UNJ Thread profilesare not interchangeable with Metric system MJ profiles or UN profile inch screws. The internal UNJ thread will assemble with the standard UN external thread however assembling external UNJ threads with UN series internal threads should be avoided due to potential interference at the minor diameter.
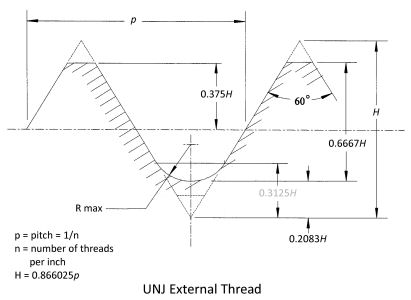
External threads are of Unified form per ASME B1.1 and modified at the root so that the flanks of the adjacent threads are joined by one continuous, smooth and blended curve tangent to the flanks. The radius is specified in the applicable standard.
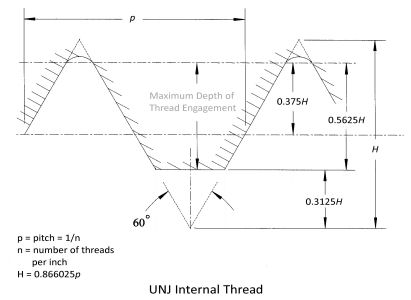
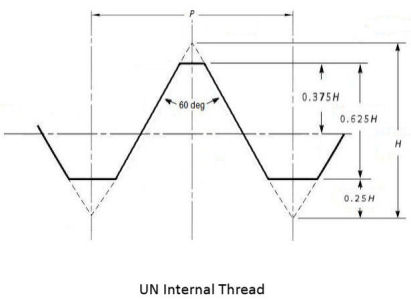
Internal threads are also of Unified form per ASME B.1. and modified at the minor diameter to the values specified in the applicable standard.
Standard working Go/No Go thread plug gages are used to inspect internal J threads. The gage is typically marked without any modifications to the Plugs.
For external J threads, the Go member is modified to clear the minor diameter. A standard No Go thread ring gagemay be used to inspect J threads. Both gages are typically marked accordingly.
Applicable Standards:
ASME B1.1 Unified Inch Screw Threads ( UN and UNR Thread Form )
ASME B1.2 Gages and Gaging for Unified Inch Screw Threads
ASME B1.3 Screw Thread Gaging System for Dimensional Acceptability – Inch and Metric Screw Threads
( UN, UNR, UNJ, M and MJ
ASME B1.7 Nomenclature, Definitions, and Letter Symbols for Screw Threads
ASME B46.1 Surface Texture ( Surface Roughness, Waviness and Lay )
ASME B47.1 Gage Blanks
WHERE
The J series thread is defined in specification ANSI/ASME SAE AS8879 (formerly MIL-S-8879) and in ANSI/ASME B1.15.
WHY
The rounded root of a UNJ external thread greatly improves fatigue strength over that of a flat root UN thread. It seems that sharp cuts at the minor diameter of the external screw thread create stress points where fractures can begin and which ultimately cause failure of the external thread. An additional benefit is that the rounded root of the UNJ thread reduces the rate of threading tool crest wear. The internal thread does not get the same rounded root treatment because the internal thread usually has more mass around the thread and is nearly impervious to stress fracturing. If you have a situation where the internal thread is made in a thin wall part and stress fracturing is a concern; there is an internal thread rounded root optionavailable, but it is not officially codified.
CLASS-OF-FIT
Typically and historically the J-series of thread has been Class-of-fit 3A and 3B. This is the only class designated in ANSI/ASME SAE AS8879. Not as common is Class-of-Fit 2A and 2B which are permitted and defined in ANSI B1.15. If you have a requirement for a J-series thread it would be best to verify the class-of-fit if it is not designated on the product drawing.
INTERNAL SCREW THREAD
The UNJ for internal threads is identical to the UN thread except that the UNJ minor diameter is slightly larger than the UN minor diameter. This is to allow the minor diameter of the internal thread to clear large root radius of the UNJ external thread. If a UNJ bolt is screwed into a UN nut there will in most cases be an interference fit at the thread minor diameter. To make the minor diameter larger use a larger size drill bit when preparing for a J-series screw thread. If you have a standard UN-series threaded hole, and you wish to have a UNJ-series threaded hole; select the proper size drill bit for the UNJ-series size and enlarge the minor diameter of the UN-series threaded hole; you now have a UNJ-series threaded hole.
EXTERNAL SCREW THREAD
Both UNJ and UN are used for external threads.
External UNJ threads per SAE AS8879 have a rounded controlled root radius at the minor diameter. The minimum root radius is calculated at 0.15011p and the maximum root radius is calculated at 0.18042p. The root contour shall have a smooth, continuous, non-reversing contour and shall blend tangentially into the flanks and any straight segment. The radius is larger than the UNR style.
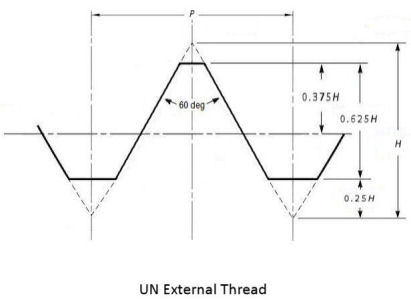
External UN threads per ANSI/ASME B1.1
Paragraph 1.3: UN threads have "a flat or optional rounded root contour" at the minor diameter.
Paragraph 2.3.1: UN threads have "a flat root contour" at the minor diameter, but "a rounded root contour cleared beyond the 0.25P flat width of the basic profile is optional"..."to provide for some threading tool crest wear."
PRODUCT COMPATIBILITY
UN Bolt into UN Nut = No problems.
UNJ Bolt into UNJ Nut = No problems.
UN Bolt into UNJ Nut = No assembly problems; functional problems are possible.*
UNJ Bolt into UN Nut = In most cases an interference fit at the thread minor diameter; functional problems are possible.*
SCREW THREAD WORK PLUG GAGES
UN = UNJ
The only difference between the internal UNJ thread and the standard UN threaded is that the UNJ thread has a larger minor diameter. The thread work plug gage does not check the minor diameter of the thread, thus when checking the threads, standard UN style Work Plug Gages are used. If UNJ gages are ordered from a gage maker, the gage maker will supply the standard UN gage members with a handle marked UNJ. The minor diameter of internal threads should be checked with plain pin gages.
SCREW THREAD RING GAGES
2A or 3A GO: UN ≠ UNJ
2A NOGO UN =or≠ UNJ (Varies by size/pitch; assume ≠.)
3A NOGO UN = UNJ
Because of the large root radius on the minor diameter of the external thread, the UNJ GO ring gage is supplied with an enlarged minor designed to clear the root radius. The GO ring gage is the only gage that is modified specifically for the UNJ specification and the only difference between the UNJ GO and the UN GO thread gages is the minor diameter. The UN GO ring gage if used to measure the UNJ thread the gage will reject the part because of the minor diameter interference. The UNJ NOGO ring gage is identical to the UN NOGO ring gage except that it may be marked with a "J". The minor diameter of the NOGO ring gage is relieved to just below the pitch diameter, and because of this the standard UN NOGO gage will clear the minor diameter of both the UN and UNJ external threads.
SCREW THREAD SET PLUG GAGES
UN = UNJ
The set plug members used for the UNJ series threads are identical to the set plugs used for the UN series. If UNJ gages are ordered from a gage maker, the gage maker will supply the standard UN gage members with a handle marked UNJ. This is because set plug gages do not check the minor diameter of the ring gage they are setting. The minor diameter of the ring gage should be checked with plain pin gages after the ring has been properly set with the set plug.
HOW TO CHECK THE ROOT RADIUS
Use an optical comparator to check the UNJ external thread form root radius at the minor diameter. The thread radius must be smoothly blended with the flank angles leaving no sharp groove or edge at the root of the thread.
THREAD NOMENCLATURE
UN = Basic Unified National thread series
UNJ = Basic Unified National thread series with external thread controlled root radius
UNS = Special Unified National thread series
UNJS = Special Unified National thread series with external thread controlled root radius
UNC = Unified National Coarse thread series
UNJC = Unified National Coarse thread series with external thread controlled root radius
UNF = Unified National Fine thread series
UNJF = Unified National Fine thread series with external thread controlled root radius
UNEF = Unified National Extra Fine thread series
UNJEF = Unified National Extra Fine thread series with external thread controlled root radius
What is meant by: Functional problems are possible.
This is one of those esoteric things; or alternately said a CYA thing on my part. Basically the two threads are not designed to be used as a connection, even though they will/may screw together. There are some physical differences in the threads which could in some extreme situation cause a problem. If you choose to use them as such you should conduct an engineering evaluation of the design parameters to assure that some minor detail will not pop-up to cause a failure of your connection. The differences in the threads are related to the minor diameter size and shape which could affect the strength of the material and/or the maximum loading of the thread (torque and/or straight pull) and/or the potential for stress cracking. All of these things are product design related and impossible for me to determine in any general statement.

